Call me - +30 6944.237.080 - +30 210.86.20.001
Carotid Diseases
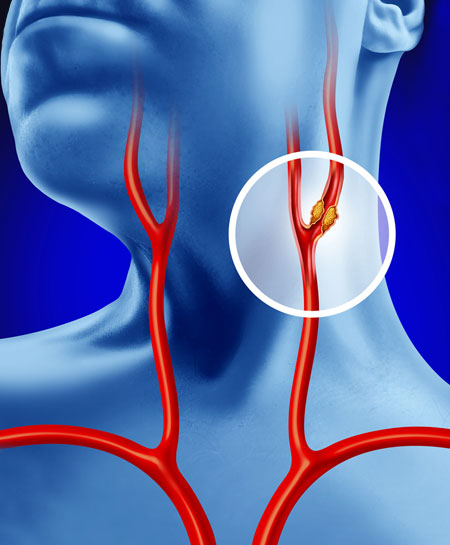
Carotid disease, also known as carotid artery disease, is a condition that affects the major blood vessels in the neck, known as the carotid arteries. These arteries are responsible for supplying oxygenated blood to the brain. When these arteries become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque, it can lead to serious health issues, including stroke. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for carotid disease to help you better understand this condition.
Causes:
Atherosclerosis: The primary cause of carotid disease is atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the accumulation of fatty deposits (plaque) on the inner walls of the arteries. Over time, this plaque can harden and narrow the carotid arteries, reducing blood flow to the brain.
Diabetes: People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing atherosclerosis, which can increase their chances of carotid disease.
High Blood Pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage the walls of the carotid arteries, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup.
Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for carotid disease. It not only contributes to the development of atherosclerosis but also increases the risk of blood clot formation, which can further block the carotid arteries.
Symptoms:
Carotid disease often goes unnoticed until it becomes severe or causes a stroke. Common symptoms include:
Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs): Also known as "mini-strokes," TIAs can cause temporary weakness or numbness on one side of the body, slurred speech, and impaired vision.
Ischemic stroke: the injuries may be irreversible, even though the symptoms can be identical to those of a transient ischemic attack.
Symptoms include::
- Speech and Language Difficulties: Difficulty in speaking or understanding speech can be a sign of reduced blood flow to the brain due to carotid disease.
- Vision Problems: Blurred vision, sudden loss of vision in one eye, or double vision may occur when the carotid arteries are severely blocked.
- Weakness or Numbness: One side of the body may become weak or numb, particularly in the face, arm, or leg.
- Dizziness or Loss of Balance: Reduced blood flow to the brain can lead to dizziness, loss of balance, or difficulty walking.
The symptoms that manifest depend on the region of the brain affected. A key feature is the abrupt onset of symptoms, which should prompt urgent medical evaluation for further care and management. For symptoms to be reversible, cerebral ischemia must be restored within 3 to 6 hours.
Treatment:
Depending on the degree of carotid stenosis, the presence or absence of symptoms, the patient’s age, and other comorbid medical conditions, the appropriate treatment is determined on a case-by-case basis under the guidance of the vascular surgeon. This may include:
Lifestyle Modifications: Managing risk factors such as smoking cessation, maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and controlling high blood pressure and diabetes can help slow the progression of carotid disease.
Φάρμακα: Medications: Doctors may prescribe medications to reduce cholesterol levels, prevent blood clot formation, and control blood pressure.
As regards surgical management, and depending on the indications, the following techniques are included:
- Carotid Endarterectomy: This surgical procedure involves removing the plaque buildup from the carotid artery to restore proper blood flow.
- Carotid Artery Stenting: A less invasive procedure, carotid artery stenting involves placing a stent (a small mesh tube) in the artery to keep it open and improve blood flow.
In both surgical methods, as with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of complications ranging from minor to severe, which will be discussed with you in detail.
Carotid disease is a serious condition that can lead to life-threatening complications like stroke. Recognizing the risk factors, understanding the symptoms, and seeking prompt medical attention can help prevent the progression of the disease and improve the chances of a successful recovery. If you or a loved one is at risk or experiencing symptoms of carotid disease, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
