Call me - +30 6944.237.080 - +30 210.86.20.001
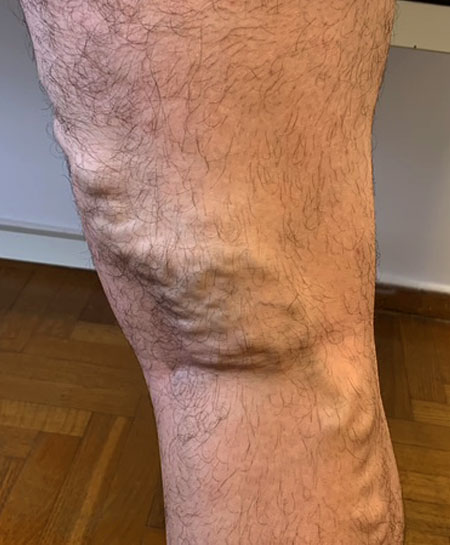
Venous Insufficiency/ Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are a common vascular condition that affects a significant number of individuals, particularly in the legs and feet. While often considered a cosmetic concern, varicose veins can also cause discomfort and lead to more serious health issues. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options available for managing varicose veins.
Causes:
Varicose veins develop when the valves in the veins fail to function properly. These valves are responsible for ensuring that blood flows in one direction, toward the heart. When the valves weaken or become damaged, blood can flow backward and pool in the veins, causing them to enlarge and become twisted.
Several factors contribute to the development of varicose veins, including:
Genetics, Age, Gender, Prolonged Standing or Sitting, female gender, pregnancy, deep vein thrombosis, smoking, trauma.
Symptoms:
Varicose veins may present with the following symptoms:
Visible, Enlarged Veins: Twisted, bulging veins are a common visual indication.
Aching or Heaviness: Discomfort or a feeling of heaviness in the affected area.
Swelling: Swelling of the legs and ankles, particularly after extended periods of standing.
Skin Changes: Skin around the veins may become discolored or develop sores in severe cases.
Bleeding from varicose veins: In many cases, varicose veins rupture and bleed as a result of the fragility of their vascular wall.
Thrombosis: Primarily in cases of extensive and large varicose veins.
Venous ulcers: Chronic wounds that are slow to heal, typically developing at advanced stages of the disease, and significantly impairing patients’ quality of life.
Treatment:
Several treatment options are available for managing varicose veins, ranging from lifestyle changes to medical interventions:
Compression Stockings: These help improve blood circulation and alleviate symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and elevating the legs can contribute to symptom relief.
Phlebotropic drugs and dietary supplements: Used for the relief of symptoms in a subset of patients, in whom they appear to be effective and provide clinical benefit.
Sclerotherapy: A medical procedure involving the injection of a solution to close off the affected vein.
Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT): A minimally invasive procedure using laser energy to seal the vein.
Saphenectomy represents the open surgical approach to the management of varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency. For many years, it was the sole modality available, and thus is considered a classic technique. It requires general anesthesia and a short inpatient stay. It is employed in complex cases that are not suitable for endovenous thermal ablation with the aforementioned Laser or RFA methods.
Mini- or microphlebectomies: their purpose is the eradication of varicose veins through very small incisions that close without sutures and do not leave scars. They may be performed as a standalone procedure or in combination with endovenous Laser, RFA, or saphenectomy.
Conclusion:
Varicose veins are a common vascular issue that can impact both physical comfort and aesthetic concerns. Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and exploring treatment options are crucial steps in managing this condition. If you suspect you have varicose veins or are experiencing related symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
